Understanding the Basics: What is a Ceiling Track Hoist?
A ceiling track hoist consists of a motor unit that travels along a fixed track system mounted to the ceiling. This motor is connected to a sling via a spreader bar, allowing for safe and comfortable transfers between beds, wheelchairs, toilets, and other locations. It empowers users to move independently or with minimal assistance, promoting dignity and reducing the risk of injuries associated with manual lifting.
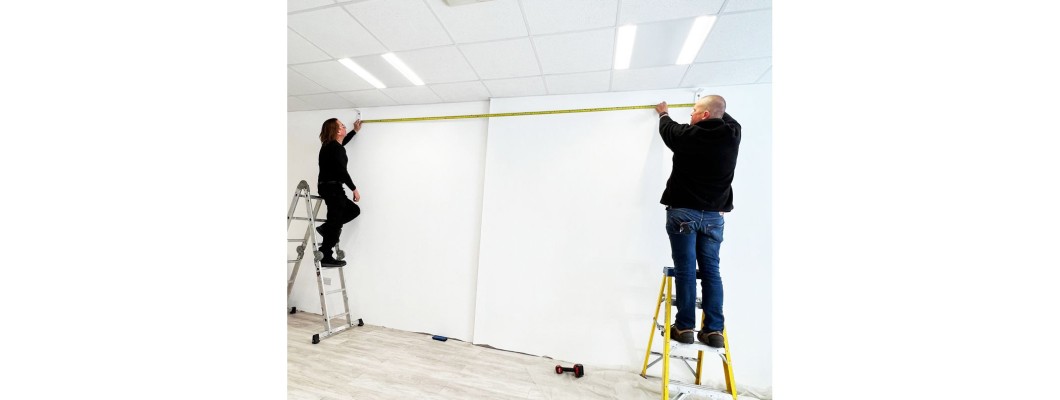
The Installation Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
Installing a ceiling track hoist requires meticulous planning and execution. While professional installation is highly recommended for safety and compliance, understanding the process can help you make informed decisions.
1. Assessment and Planning:
- Structural Evaluation: The first step involves assessing the ceiling's structural integrity. A qualified professional will determine if the ceiling can support the weight of the hoist system and the user. This may involve inspecting joists, beams, and other structural elements.
- Layout Design: A detailed layout of the track system is crucial. This involves considering the user's transfer needs, the room's dimensions, and any obstacles. The goal is to create a seamless and efficient transfer pathway.
- Power Supply: Ensuring a reliable power supply is essential. Electrical connections must be made by a qualified electrician, adhering to local building codes and safety regulations.
- User Needs: The specific needs of the user should be at the forefront of the planning process. Consider their weight, transfer requirements, and any specific medical conditions.
2. Track Installation:
- Marking and Drilling: Once you have agreed, the ceiling is marked for drilling. Precision is paramount to ensure proper track alignment.
- Fixing Points: Appropriate fixing points are installed to secure the track to the ceiling. This may involve using threaded rods, expansion bolts, or other specialized fixings, depending on the ceiling material and structural requirements.
- Track Assembly: The track sections are assembled and connected, ensuring a smooth and continuous pathway. Leveling and alignment are critical for optimal motor movement.
- Support Structures: In some cases, additional support structures may be required to reinforce the ceiling or bridge gaps between joists.
3. Motor and Sling Installation:
- Motor Mounting: The motor unit is attached to the track, ensuring it moves freely along the pathway.
- Electrical Connections: The motor is connected to the power supply, and safety checks are performed to ensure proper functionality.
- Spreader Bar and Sling Attachment: The spreader bar is attached to the motor, and the appropriate sling is selected based on the user's needs.
- Testing and Calibration: The entire system is thoroughly tested to ensure smooth operation, proper weight capacity, and safety features.
4. Training and Handover:
- User Training: The user and caregivers receive comprehensive training on how to operate the hoist system safely and effectively.
- Maintenance Instructions: Clear instructions are provided on routine maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Documentation: All installation details, including structural assessments, electrical connections, and testing results, are documented for future reference.
Straight Rail vs. XY System: Understanding the Differences
Choosing between a straight rail and an XY system is a crucial decision that impacts the system's functionality and user experience.
Straight Rail System:
- Description: A straight rail system consists of a single track that runs in a linear direction. It is ideal for transfers along a single axis, such as between a bed and a wheelchair or from a toilet to a shower.
- Advantages:
- Simpler installation and lower cost compared to XY systems.
- Suitable for straightforward transfers in confined spaces.
- Requires less ceiling space.
- Disadvantages:
- Limited movement range, restricting transfers to a single direction.
- May require multiple straight rail systems for complex transfer needs.
- Less flexible than an XY system.
XY System:
- Description: An XY system consists of two opposite tracks and a track that connects to both, which is called a traverse rail. The traverse rails roll up and down the room, forming the H or XY System. This allows the HOIST POD to move left to right on the traverse rail, providing complete room coverage.
- Advantages:
- Enhanced flexibility and freedom of movement, enabling transfers to any point within the room.
- Ideal for complex transfer needs and larger spaces.
- Reduces the need for multiple hoist systems.
- Safely place users on and off the floor
- Disadvantages:
- More complex installation and higher cost compared to straight rail systems.
- Requires more ceiling space and structural support.
- It may be overkill for simple transfer needs.
Key Considerations for Choosing the Right System:
- User Needs: The user's specific transfer requirements should be the primary consideration. If transfers are limited to a single direction, a straight rail system may suffice. For more complex needs, an XY system is recommended.
- Room Size and Layout: The room's dimensions and layout play a crucial role in determining the appropriate system. Larger rooms and complex layouts benefit from XY systems, while smaller rooms may be better suited for straight rail systems.
- Budget: Straight rail systems are generally more cost-effective than XY systems. Consider your budget and the long-term benefits of each system.
- Ceiling Structure: The ceiling's structural integrity is essential for supporting the weight of the hoist system. An XY system typically requires more robust support than a straight rail system.
- Future Needs: Consider the user's potential future needs and how the system may need to be adapted. An XY system offers greater flexibility for future adjustments.
Essential Safety Features:
- Emergency Stop: A readily accessible emergency stop button is crucial for the immediate halting of the motor.
- Overload Protection: This feature prevents the motor from lifting excessive weight, ensuring user safety.
- Low Battery Alarm: A low battery alarm alerts caregivers when the motor's battery needs charging.
- Anti-Sway System: Some advanced systems incorporate anti-sway features to minimize movement during transfers.
- Safety Interlocks: Prevents the motor from operating if the sling is not properly attached.
Maintenance and Care:
- Regular Inspections: Routine LOLER inspections should be conducted to ensure the system's functionality and safety.
- Cleaning and Lubrication: Regular cleaning and lubrication of the track and motor components are essential for smooth operation.
- Professional Servicing: Periodic professional servicing is recommended to address any potential issues and ensure compliance with safety standards.
The Impact on Quality of Life:
Ceiling track hoists can significantly enhance the quality of life for individuals with mobility challenges. They promote independence, dignity, and safety, reducing the physical and emotional strain associated with manual lifting. By carefully considering the installation process and system differences, you can select the optimal solution for your specific needs, creating a more comfortable and accessible environment.
Conclusion:
Installing a ceiling track hoist is a significant investment that requires careful planning and execution. By understanding the installation process, the differences between straight rail and XY systems, and the essential safety features, you can make informed decisions that prioritise the user's needs and create a safe and comfortable environment. Professional installation is highly recommended to ensure compliance with safety standards and optimal system performance. By embracing this technology, you can empower individuals with mobility challenges to live more independent and fulfilling lives.
If you would like a free survey, please click here...